
Introduction of Spinach Farming:- Spinach is one of the perennial leafy vegetable and grown throughout the world. Spinach has an excellent nutrition values and health benefits. Farmers can grow this crop in greenhouse, poly house and hydroponic system as well. Spinach can be gown for daily use in pots, containers, back yards. Spinach belongs to the family of “Amaranthaceae” and genus of Spinacia”. Spinach is thought to have originated in ancient Persia as a wild plant (modern Iran and neighboring countries). Spinach is native to central and western Asia. When it comes to the spinach plant characteristics, it is an annual plant and grows up to 30 cm tall in height. The spinach leaves are alternate, simple, ovate to triangular, and very variable in size from about 2 cm to 25 cm long and 1 cm to 14 cm broad, with larger leaves at the base of the spinach plant and small leaves higher on the flowering stem of the plant. The spinach flowers are inconspicuous, yellowish-greenish, 3 mm to 4 mm in diameter, maturing into a small, hard, dry, lumpy fruit cluster 5 mm to 10 mm across containing several seeds. Following best farming methods and choosing right commercial/hybrid variety will be success factor in spinach farming.

Health Benefits and Nutrition Facts of Spinach:- The following are the health benefits of Spinach.

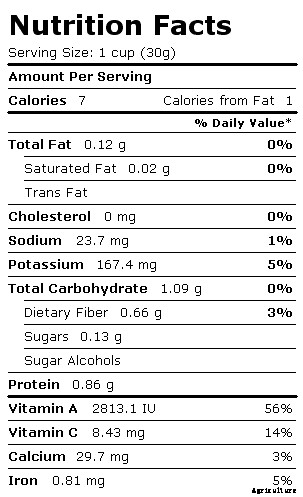
The following is the nutrition chart of spinach.
Top 10 Producers of Spinach in the World:- China, United States, Japan, Turkey, Indonesia, Iran, Pakistan, France, Korea and Belgium.
Major Spinach Production States in India:- The popular spinach/palak growing states include Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Maharashtra and Gujarat.
Local Names of Spinach in Asia:- бууцай, Buutsai (Mongolian), Palak (Urdu), 시금치, Sigeumchi (Korean), पालुङो, Palak (Nepali), Espinaca (Spanish), cây rau bina (Uzbek), السبانخ (Arabic), спанак, spanak (Bulgarian), 菠菜,bō cài (Chinese), Mchicha (Filipino), ผักขม, pàk kŏhm (Thai), rau bina (Vietnamese), ほうれん草 (Japanese), නිවිති, Nivithi (Sinhalese, Sri Lanka),špenát (Czech),Шпинат,špinát (Russian), spenat (Swedish),ıspanak (Turkish), Spenót (Hungarian), Bayam (Malay), اسفناج ,esfenâj (Persian), 菠菜 (Taiwanese).
Local Names of Spinach in India:- Palak (Hindi), Palakura (Telugu), பசலைக்கீரை, Pasalai Keerai (Tamil), Cheera,ചീര (Malayalam), પાલક, Palak (Gujarati), ਪਾਲਕ, Paalak (Punjabi), Palak (Manipuri), palanga saga (Oriya), Palaeng Xaak (Assamese), ಪಾಲಕ್ ಸೊಪ್ಪು,Palak Soppu,Basale Soppu (Kannada), पालक, Palak (Marathi), পালং শাক, Palong Shak (Bengali), Paalakh (Kashmiri).
Varieties of Spinach:- There are many improved varieties available in Asia, however, it is very important to find out the suitable cultivar for your region. Contact local horticulture department for suitable cultivar.

Climate and Soil Requirements for Spinach Farming:- Although spinach beet is a winter season crop, it can be grown throughout the year under mild temperature conditions. The best part of it is, this leafy vegetable crop can tolerate frost better than other vegetable crops. Spinach crop also tolerates warm weather but high temperatures leads to premature bolting without giving economic yield. Spinach can be cultivated on wide range of soils having good fertility and well-drainage. However, sandy loam soils are most suitable for its cultivation. Although, spinach can tolerate slightly alkaline soils, the best yield and quality of greens can be expected in neutral soils having a pH of 6.0 to 7.5.

Land Preparation in Spinach Farming:- The land or main filed should be ploughed 5 to 6 times to make the soil soft and bring it to fine tilth stage. Make sure to level the land and remove the weeds from previous crops. After soil testing, micronutrients should be added in case of any deficiency soil nutrients. The beds and irrigated channels should be made.
Propagation in Spinach Farming:- Generally, propagation in spinach farming is done through seeds.

Seed treatment in Spinach Farming:- Spinach seed rate depends on crop season and variety of spinach grown. Generally, for winter crop, use 15 to 20 kg seeds /ha and for summer crop 30 to 40 kg/ha is required.
Sowing and Spacing in Spinach Farming:- The main sowing season in plains is from last week of Aug to 2nd week of Nov month. In places with mild climate, it may grow throughout the year. In hilly regions, spinach is sown from March to May. To improve germination, seeds are soaked in water overnight before sowing. Sowing can be done either by broadcast method or by line sowing. Line sowing is more desirable as it facilities weeding, hoeing and harvesting. Line spacing should be maintained at 25 cm and thinning should be done to maintain plant spacing within lines at about 5 cm.
Manures and Fertilizers in Spinach Farming:- As spinach is a leafy vegetable, its crop requires more nitrogen for crown growth. If you are going for commercial spinach farming, it is better go for soil testing and fertilizers should be applied based on the soil analysis. Usually 25 tonnes of well-rotten farmyard manure (FMY), along with 90 kg of ‘N’ and 30 kg of ‘P2O5’ /ha should be applied. It is advised to supplement the whole of farmyard manure and P205 and 1/2 (half) of ‘N’ dose at the time of land preparation. The remaining 1/2 (half) ‘N’ can be applied in 2 split doses, one after each cutting/harvesting followed by a light irrigation in the field.

Irrigation in Spinach Farming:- Irrigation in spinach farming should be given based on soil (moisture holding capacity) and climatic conditions. Irrigate the spinach plant filed immediately after sowing the spinach seeds. Provide subsequent irrigations at an interval of 3 to 4 days during summer and 6 to 8 days during winter. However, rainy season crop does not require much irrigation.
Intercultural operations in Spinach Farming:- In spinach farming, hand weeding is essential to control weed apart from giving 3 to 4 hoeing. This process also helps in loosening the soil for proper aeration.
Pests and Diseases in Spinach Farming:- Well, as spinach is a leafy vegetable, there can be many varieties of pests and disease can attack the spinach crop. The following are the common pests and disease found in spinach farming.
Harvesting in Spinach Farming: – Spinach will be ready for harvesting in an about 4 to 5 weeks after sowing of spinach seeds. Subsequent cuttings should be taken at an interval of 20 to 24 days depending upon variety and season. It is recommended to harvest early in the morning because there is dew on the crop. After harvesting, spinach leaves should be washed off and trimmed. To market the spinach, the leaves should be graded and bunched based on quality.
Yield in Spinach Farming:- Well, crop yield depends on the variety and farm management practices. Usually, an average of 60 to 80 quintals of green leaves per hectare land can be expected in spinach farming.
Marketing in Spinach Farming:- Make the bundles and transport to local markets before they start producing seeds.
For Sheep or Goat Farming : Read here.
For Indian Agriculture : Read here.