Today, we discuss the topic of the biogas production process along with types of biogas plants, working principles of biogas, biogas plant cost in India, advantages of biogas. We also include a biogas plant diagram for your reference. why wait, let us dive into the steps involved in the Biogas production process.
Biogas is a biofuel and it normally refers to the gas produced from organic matter as it is broken down by biological means. Biogas can be produced by anaerobic digestion or fermentation of biodegradable materials such as biomass, manure, sewage, municipal waste, cattle dung, green waste and energy crops. The production of biogas can be naturally produced from the decomposition of organic waste. When organic matter, such as food scraps and animal waste, break down in an anaerobic environment that means an environment absent of oxygen they release a blend of gases, primarily methane and carbon dioxide.

The biogas formed from a digester is comprised primarily of methane, carbon dioxide, and other trace gases. A biogas plant generates biogas from organic substances such as cattle –dung, and other biodegradable materials such as biomass from farms, gardens, kitchens and night soil wastes, etc. The process of biogas generation is known as anaerobic digestion (AD).
Biogas production is primarily Methane and Carbon dioxide. It could have small amounts of hydrogen sulfide moisture and siloxanes. The primary gases methane, hydrogen and carbon monoxide can be combusted or oxidized with oxygen. This energy release allows biogas to be used as a fuel; it can be used for any heating function, such as cooking. Biogas can be used in a gas engine to convert the energy in the gas into electricity and heat.
Approximately, the production of biogas in India is about 20,757 lakh cubic meters in 2014-15. This is equivalent to 6.6 crores domestic Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) cylinders. This is equivalent to 5% of the total LPG consumption in India today.
Within states, Maharashtra tops the production biogas with 3578 lakh cubic meters while Andhra Pradesh comes next with 2165 lakh cubic meters.
The principle of biogas production will be given below;
Biogas is formed as a result of anaerobic fermentation of biomass in the presence of water.
Some of the benefits of the biogas technology are given below;
You may also like Solar Subsidy, Loan Schemes for Rooftop and Agriculture.
There are mainly two types of biogas plants in usage for the production of biogas. These are:
The fixed dome type biogas plant consist of a closed underground digester tank made up of bricks which has a dome-shaped roof made up of bricks. This dome-shaped roof of the digester tank functions as a gas holder and has an outlet pipe at the top to provide gas to homes.
The slurry is formed by mixing water in cattle dung in equal proportion in mixing tank. The formed slurry is then sent into the digester tank with the help of the inlet chamber. It must be noted that slurry is fed into the digester tank up to the point where the dome of the roof starts. Inside the digester tank, the complex carbon compounds are present in the cattle dung breaks into simpler materials by the action of anaerobic microorganisms in the presence of water. This anaerobic decomposition of complex carbon compounds present in cattle dung produces biogas and gets finished in about 60 days. The produced biogas starts to collect in the dome-shaped roof of biogas plant and is supplied to homes through pipes. The spent slurry is replaced with fresh slurry in time to time and continue the production of biogas.
The floating gas holder type biogas plant consists of a dome-shaped gas holder made of steel and for collecting biogas. This gas holder is not fixed but is moveable and floats over the slurry present in the digester tank. Due to this explanation, this biogas plant is called the floating gas holder type biogas plant.
The slurry is formed by mixing water in cattle dung in equal proportion in mixing tank. The slurry is then injected into a digester tank with the use of the inlet pipe. The digester tank is a closed underground tank prepared up of bricks. Inside the digester tank, the carbon compounds present in the cattle dung breaks into simpler compounds by the action of anaerobic microorganisms in the presence of water. This anaerobic decomposition of complex carbon compounds present in cattle dung generates biogas and gets completed in about 60 days. The biogas starts to collect in floating gas holder and is supplied to homes through pipes. And the spent slurry is replaced with fresh slurry to continue the production of biogas.
Important raw materials for biogas production are given below;
Biogas is produced either;
Biogas is known as an environmentally-friendly energy source because it alleviates two main environmental problems simultaneously:
By converting organic waste into energy, biogas is utilizing nature’s elegant tendency to recycle substances into useful resources. Biogas generation recovers waste materials that could otherwise pollute landfills; prevents the usage of toxic chemicals in sewage treatment plants, and saves money, energy, and material by treating waste on-site. Also, biogas usage does not require fossil fuel extraction to produce energy.
Instead, biogas takes a problematic gas and changes it into a much safer form. More specifically, the methane content there in decomposing waste is converted into carbon dioxide. Methane gas has roughly 20 to 30 times the heat-trapping capabilities of carbon dioxide. This means that when a rotting loaf of bread converts into biogas, the loaf’s environmental impact will be about ten times less potent than if it was left to rot in a landfill.
You may also check Dairy Animal Feed, Nutrition Management.
To produce biogas, organic ferments with the help of bacterial communities. Four stages of fermentation move the organic material from their primary composition into their biogas state.
The biogas plant receives all kinds of organic waste and typically livestock manure and organic industrial waste. The dry solid in livestock manure contains carbon, among other things, and in the process, the carbon is transformed into biogas, a compound of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
The manure and waste are mixed in the plant’s receiving tank before being heated to 38 to 52°C or 100-125.6°F and pumped into the digester in which the biogas is produced. The biomass stays in the digester for 2 to 3 weeks and the fermented slurry can subsequently be used as crop fertilizer. This fertilizer has better qualities such as fewer odor inconveniences when spreading the slurry and significant reduction of greenhouse gasses.
The biogas plant is a brick and cement structure having the below five sections:
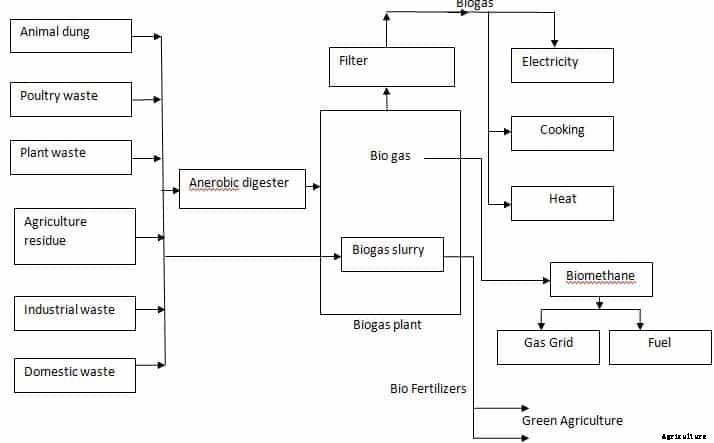
Let us discuss the working of a biogas plant;
In the working of biogas plant firstly the fresh animal manure is stored in a collection tank and before its processing to the homogenization tank which is prepared with a mixer to facilitate homogenization of the waste stream. The uniformly mixed waste is passed through a macerator to get uniform particle size of 5-10 mm and pumped into suitable-capacity anaerobic digesters where stabilization of organic waste takes place.
In anaerobic digestion, organic material is converted to biogas by a series of bacteria sets into methane and carbon dioxide. The majority of commercially operating digesters are plugging flow and complete-mix reactors operating at mesophilic temperatures. The type of digester used changes with the consistency and solids content of the feedstock, with capital investment factors and with the primary purpose of anaerobic digestion.
Biogas can be used to work a dual-fuel engine to replace up to 80 % of diesel oil. Diesel engines have been modified to run 100 percent on biogas production. Petrol and CNG engines can be modified easily to use biogas. A special adapter can be fitted to LPG Genset to enable process with biogas. Importing a small biogas Genset directly from Bangladesh could be the cheaper alternative until a suitable product is developed in India.
The below points are explained about working of biogas plant;
You may also refer to Briquetting Process Technology.
Theoretically, biogas can be converted into electricity by using a fuel cell. However, this procedure requires very clean gas and expensive fuel cells. Hence, this option is still a matter for research and is not currently a practical option. The conversion of biogas to electric power by a generator set is more practical. In contrast to natural gas, biogas is characterized by a high knock resistance and thus can be used in combustion motors with high compression rates.
In most cases, biogas is used as fuel for combustion engines, which convert it to mechanical energy, powering an electric generator to create electricity. The design of an electric generator is related to the design of an electric motor. Most generators create alternating AC electricity; they are therefore also called alternators or dynamos. Appropriate electric generators are obtainable in virtually all countries and in all sizes. The technology is well known and maintenance is very simple. The combustion engine using the biogas as fuel. In theory, biogas can be used as fuel in nearly all types of combustion engines, such as gas engines or Otto motor, diesel engines, gas turbines, and Stirling motors, etc.
The cost of biogas plant changes from place to place and size of the plant. The average cost of two cubic meter size biogas plant is about Rs. 17,000/-. It is normally high about 30 percent more in hilly areas and about 50 percent more in the North Eastern Region States.
Biogas is not typically produced at the time or in the quantity required to satisfy the conversion system load that it serves. When this occurs, storage systems are employed to smooth out variations in gas creation, gas quality, and gas consumption. The storage component acts as a reservoir, allowing downstream equipment to operate at a constant pressure.
Wide selections of materials have been used in making biogas storage vessels. Medium-and high-pressure storage vessels are normally constructed of mild steel while low-pressure storage vessels can be made of steel, concrete, and plastics. The newest reinforced plastics feature polyester fabric which appears to be appropriate for flexible digester covers. The delivery pressure necessary for the final biogas conversion system affects the choice for biogas storage.
You may also like Smart Farming in India.

That’s all folks about Biogas production process and advantages. Keep producing natural energy.
You may be interested in Growing Onions from Sets and Seeds.