Cold chain is an integrated support system that reduce waste in fresh produce. According to studies 50% of fresh vegetables/fruits, 30% fish and 20%meat are lost from production to consumption. This is truer in African countries with challenges in cold chain system.
The term implies the use of low temperature control to reduce rotting and extend shelf life of products through the harvest, storage, transportation and marketing. Essentially logistic based the value chain supports different freezing technology to accommodate diverse products.
Types of agricultural products in cold chain system
Type of agricultural products in the system are perishable items like fresh vegetables, fruits, seafood and livestock carcass. Cold chain also refer to non-agricultural products that require low temperature environment. Items such as pharmaceuticals (vaccines), chemicals, photographic films.
Products in cold chain system
Agricultural produce
Non-agricultural products
Importance of cold chain system
Fresh food throughout their shelf life from moment of slaughter or harvest begin to deteriorate. The deterioration is possible because of rapid consumption of nutrients to simple compounds. Other activities on fresh farm produce include microbial degradation and enzyme breakdown which causes degradation in food quality.
The application of cold chain lowers temperature preserving the nutrients, texture, color, flavor and freshness of the produce. Temperatures below 10C is sufficient to preserve shelf life of most produce under tropical or subtropical temperatures.
Why Food Products Decay
Food products decay because of the presence of micro- organisms. Causes include rots, molds, fungi and bacteria. Physical manifestations of decay in food stuff are darkening, color change, bad smell, wilting, water loss and shrinking. Interventions through temperature control adversely preserves the nutritional value.
Causes of food decay
Physical manifestations of decay
Benefits of cold chain
Cold chain system delays ripening while preserving the natural senescence. It reduces ethylene production, respiration, water loss and slows ripening. Others are increases resistance to ethylene action, reduces micro-organism. Preserves nutrients, flavor and texture. Low temperatures ultimately increases shelf life and market value of food stuffs.
How to Start Cold Storage Business
Benefits of cold chain system
Use of cold chain
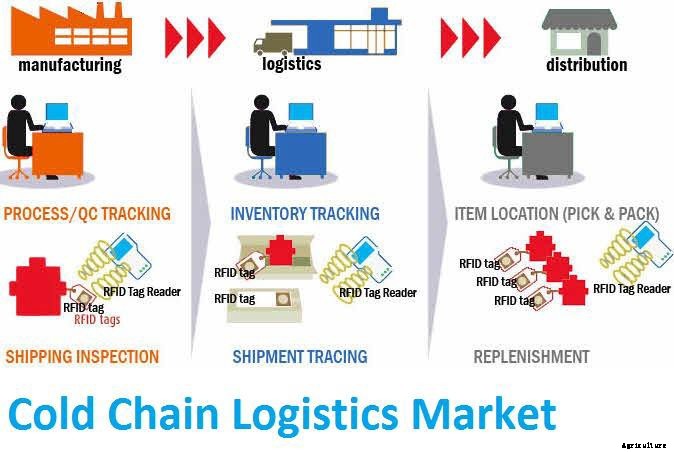
Cold chain involves the uninterrupted postharvest value chain of perishable goods. The value chain starts from the harvesting or slaughter, handling or collection to packaging and processing. Next stage is the storage facility, transportation, marketing and consumer. The system effectively manages movement of perishable goods from harvest through to consumer.
Segments of integrated cold chain are packaging, cooling, processing, cold storage, warehousing, distribution and marketing. The entire purpose of the chain system is to maintain freshness and integrity of fresh farm produce through effective management of each segment of the operation. The fresh produce are kept in optimum temperature through the supply chain till consumed.
Use
Technical logistics and Investment in cold chain
An integrated cold chain system is made up of many parts. Each part of the chain presents good economic opportunities for local investors. Major segments of an integrated system involves packaging then cooling of food produce, food process and freezing. Segments include cold storage, distribution and marketing.
Effect of low temperature on farm produce
Types of cooling
There are different types of cooling from mechanical to non-mechanical cooling. Types of cooling are evaporative cooling (evaporation of water 2-3C), slurry ice and radiant cooling. Others are solar powered cooling system, passive cooling, freezing, blast freezing.
Cooling technology for cold chain
There are a wide range of technology available through the value chain. Technology involves the handling process, processing, storage and transportation of fresh food. Technology are either expensive high technology or low technology depending on the application.
Low cooling technology are ice box, small walking cold rooms, chillers, freezers, evaporator coolers. High cooling technology vacuum cooling system, forced air system, hydro-cooling, refrigerated warehouses, blast freezers, trailer mounted refrigeration system.
Technology cooling systems
Low technology
High cooling technology
Transport cooling systems
Cooling technology of small and large scale enterprise
Non-Technical Cooling Technology
Both small and large scale operations also use non-technological cooling systems. Small scale operations use force air cooling system for pre-cooling while large scale use slurry ice. Cold storage provisions for small scale are underground storage, radiant cooling, solar chillers and night ventilation.
Some large scale operations use underground storage, radiant cooling, evaporated cooled warehouse or high altitude storage. There are no non- technology available for processing chilling or freezing. Refrigeration transport system for small scale is evaporated cooler while large scale use passive coolers.
How to start Dal Milling Business
Non-Technology based cooling systems
Conclusion
To boost efficiency along the value chain training, capacity building and implementation or adoption of cold chain system is imperative. Training involves energy efficiency, food safety, improvement on basic practices. Others are technical support, effective management of labor, finance and marketing.