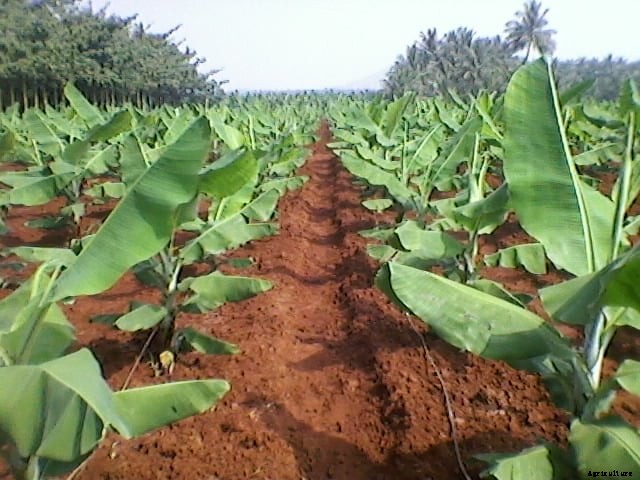

Introduction of Banana Farming:- Banana is one of the major and economically important fruit crop of Asian countries. Banana occupies vast area among the total area under crop cultivation in Asia region. Bananas are the fourth largest fruit crop in the entire world and most of Banana is cultivated by planting suckers. As technology development in agriculture is very fast, it results in developing tissue culture technique. Growing bananas does not require much effort but to achieve high yields or production requires dedication, farm management skills, and proper planting methods. Banana plant belongs to the family of “Musaceae” and genus of “Musa”. Bananas are indigenous to the tropical portions of India, Southeast Asia and northern Australia. Basically banana plants are not trees but giant herbs, which will reach their full height of between 10 feet and 20 feet after only a year. Every banana blossom develops into a fruit and ripe enough for consumption after about 4 to 5 months. After producing banana fruit, the plant stems die off and they will be replaced by new growth. The number of bananas produced by each plant varies based on fruit variety and other factors. Apart from being consumed as a fresh fruit, Banana leaves are used worldwide as cooking materials, plates, umbrellas, seat pads for benches, fishing lines, clothing fabric.
Health Benefits of Banana:- The following are the health benefits of Banana.

Local Names of Banana in Asia:- Banana (English), 바나나 (Korean), Kera (Nepali), Kela (India), Mawz,مَوْز(Arabic), Saging (Filipino), Xiāngjiāo (Chinese), Kluai (Thai), Chuối (Vietnamese), Kesel (Sinhalese, Sri Lanka),ばなな (Japanese),,ចេក, Chek (Combodian), Muz (Turkish),Банан (Russian), Kinciof (Taiwanese), Moz (Persian).
Common/Local Names of Banana in India:- Kela (Hindi), Yethampazham (Malayalam), Vazhaipazham (Tamil), Balehannu (Kannada) Arati pandu (Telugu), Kele (Marathi), Kella (Punjabi), Kadali (Oriya), Kela (Gujarati), Lafoi (Manipuri), Khiel (Kashmiri), Kellin/केळें (Konkani), Kale/কলা (Bengali), Kôl (Assamese), Kela (Urdu).
Major Producers of Banana:- Banana is one of famous tasty fruit in all over the world having a great importance in other fruits due to its health benefits and uses. There are several countries which are in production of bananas. India is no.1 producer of banana in the world. Here is the list of top producers of banana.
1. India.
2. China.
3. Uganda.
4. Philippines.
5. Ecuador.
6. Brazil.
7. Indonesia.
8. Colombia.
9. Cameroon.
10. Tanzania.
Varieties of Banana:– There are many varieties of banana grown across Asia. However, some of the popular varieties of banana are Red banana, Nyali, Safed Velchi, Basarai, Ardhapuri, Rasthali, Karpurvalli, Dwarf Cavendish, Robusta, Monthan, Poovan, Nendran, Grandnaine, Karthali, Dwarf Cavendish, Robusta, Monthan, Poovan, Nendran, Red banana, Nyali, Safed Velchi, Basarai, Ardhapuri, Rasthali, Karpurvalli, Karthali and Grandnaine, Emas, Rastali, Raja Awak, Abu, Nangka and Tanduk. Out of all these, Grandnaine is gaining popularity and may soon be the most preferred cultivar due to its tolerance to biotic stresse and good quality of bunches.
Climate Requirement for Banana Farming:- Banana is basically a tropical crop, grows well in temperature range of 14ºC to 38ºC with RH regime of 75% to 85%.Bananas need warm climate, adequate moisture and protection from wind. Chilling injury occurs at temperatures below 12ºC. The normal growth of the banana begins at 18ºC, reaches optimum at 28ºC, then declines and comes to a halt at 38ºC. Although Bananas grow best in bright sunlight, higher temperature causes sun scorching. High velocity winds which exceed 80 km/hr damage the banana crop.
Soil Requirement for Banana Farming:- Banana can be cultivated on wide range of soils. However, rich, moisture and well-drained soils with 45% clay, 70% silt, 80% loam are best for its growth. Banana plants prefer a more acidic soils with pH between 6 .5 to 7.5. Soils with low pH value make banana plants more susceptible to Panama disease. Sandy, salty, nutritionally deficient and ill-drained soil, low laying areas, black cotton soils with poor drainage should be avoided for banana farming. Supplement the soils which are deficient in nutrients with organic matter before planting the Banana trees. Banana plants require thick mulching for retaining the water and this process should be repeated as often as possible. Banana plants are very sensitive to waterlogging, because its roots will rot. This however can be resolved by planting the banana in raised beds. If you are planning for a commercial banana farming, it is advised to go for soil test.
Propagation in Banana Farming:- Generally, Propagation in Banana Farming is done by suckers or tissue culture plants.
Land Preparation In Banana Farming:- Growing green manuring crops like cowpea or daincha and burying it in the soil before the planting the banana is beneficial. The main field should be levelled and make weed free by give 3 to 4 ploughings and using harrow or rotavator or any suitable agriculture equipment to bring the soil to fine tilth stage. During the final plough, apply well rotten farmyard manure (FMY) as a basal dose in the soil and make sure it will be mixed well into the soil. A required pit size of 45 x 45 x 45 cm should be dug. These pits should be re-filled with topsoil along with well-decomposed farm yard manure of (FMY), 250 grams of Neem cake, and 20 grams of conbofuron. For better aeration and to prevent any soil borne diseases, these prepared pits should be exposed to sunlight for some time. This also kills any harmful insects. In case of saline or alkali soils having pH above 8.0, the pit mixture should be modified to incorporate organic matter. Adding more organic manure will reduce the salinity. Alternatively, planting can be done in furrows.
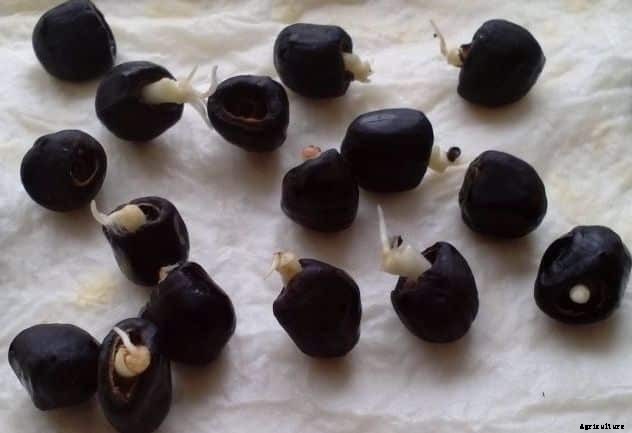

Planting Material in Banana Farming:- Suckers weighing approximately 500 to1000 grams are commonly used in propagating. The best way is to start with tissue culture plantlets. Tissue culture plantlets are recommended for planting because suckers, in general, are infected with some soil-borne pathogen and nematodes. Similarly due to the variation in age and size of sucker the crop will not be uniform, harvesting of the crop will be prolonged and crop-management becomes very difficult. Hence, tissue culture plants are recommended for planting.

Advantage of Tissue Culture:- The following are the advantages for going for Tissue culture plants in banana farming.
Planting in Banana Farming:-
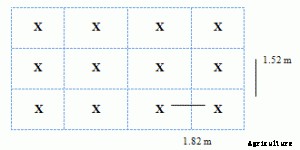
Crop Geometry
Irrigation in Banana Farming:- Generally, banana is a water loving plant and requires a large quantity of water for maximum productivity. These plants require a minimum of 2000 mm to 2500 mm annually or 25 mm per week. Deep watering should be provided during draught conditions to help leach the soil of salt. It is common that, banana plants do not bear fruits without proper irrigation. However, do not provide over irrigation as excessive water will cause roots to rot as banana roots are poor withdrawal of water. Irrigate the plants immediately after planting in the field. Apply sufficient water and maintain field capacity. In commercial cultivation of banana, an effective way of irrigation should be identified. The best method is going for drip irrigation as it has excellent advantages over conventional irrigation. Drip irrigation controls the water to be flown and the water will effectively used at the root system and it is very use full in areas where water scarcity problem exists.
Intercultural Operations in Banana Farming:- The following are the intercultural operation should be carried out on regular basis for better growth and production.

Manures and Fertilizers in Banana Farming:- Basically , Bananas crop requires nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium with a ratio of 3:1:6 and other micronutrients to ensure the plants grow vigorously. These can applied based on weather condition and plants age.
Pests and Diseases in Banana Farming:- Banana plants are more prone to viral diseases, fungal diseases and insect pests. Because of this, there will be a huge impact on fruit size, quality and yield. The below given are major pest and diseases found in banana farming. For control measures of these pests and diseases, contact local department of agriculture or any agricultural university.
Pests Viral Diseases Fungal Diseases Aphids Banana Bunchy Top Virus Head rot Fruit scarring battle Banana Bract Mosaic Virus Panama wilt Nematodes Banana Mosaic Virus Sigatoka leaf spot Pseudostem weevil Banana Streak Virus – Rhizome weevil – – Thrips – –Harvesting in Banana Farming:- The banana crop will become ready for harvesting within 11 to 12 months of planting. First ratoon crop would be ready by 8 to 10 month from the harvesting of the main crop and second ratoon by 8 to 9 months after the second crop. Harvest when fingers are fairly evenly rounded. General practice is to harvest when fingers of second hand are 3/4 rounded. Alternative, for tree-ripened fruit, cut only those hands that are ripen and leave the remaining for other day. These Bananas taste the best. However, this process is time consuming and not feasible. The mother plant should be cut off after harvest as the plant can never produce again. Harvest may be delayed up to 100 to 120 days after opening of the first hand. Harvested bunch should generally be collected in well padded tray or basket and brought to the collection site. Bunches should be kept out of light after harvest, since this hastens ripening and softening.
For local consumption, 6 to 15 hands should be often left on stalks and sold to retailers or in local markets. For exporting, hands should be cut into units of 4 to 16 fingers, graded for both length and girth, and carefully placed in polylined boxes to hold different weight depending on export requirements.
Yield in Banana Farming:- In banana Farming, over a period to 28 to 32 months, it is possible to harvest 3 crops i.e. one main crop and two ratoon crops. Under drip irrigation combined with Fertigation yield of banana as high as 100 tonnes per ha can be obtained with the help of tissue culture technique. The result would be similar yield in the ratoon crops, if the crop is managed well.
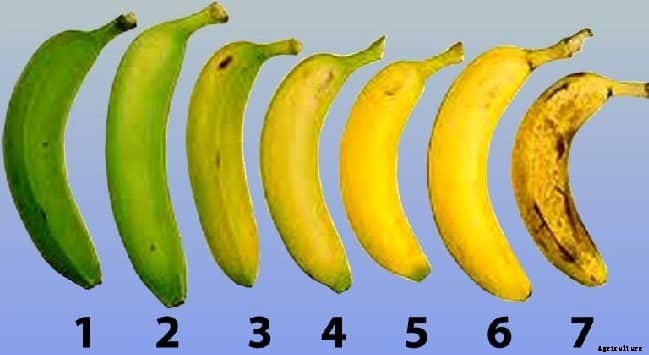
Post Harvesting Tasks in Banana Farming:- For export marketing, banana bunch are usually de-handed and soaked in sodium hypochlorite solution to remove the latex and should be treated with thiobendasole. Both sodium hypochlorite and thiobendasole are chemical compound or commonly known as bleach.
For Indian Agriculture : Read here.
For Sheep or Goat Farming : Read here.