The following article details about “Groundnut Farming” or “How to Grow Peanuts”.
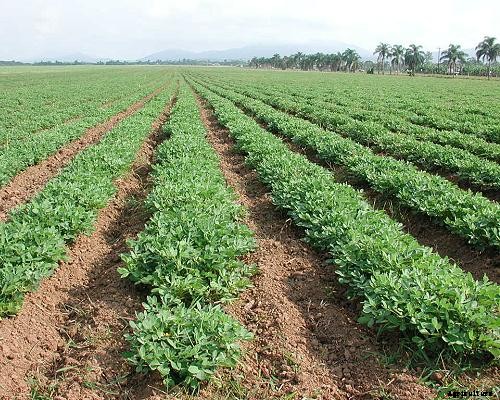

Groundnut is perfectly grown in well-drained sandy loam or sandy clay loam soil. Deep well-drained soils with a pH of 6.5-7.0 and high fertility, are ideal for groundnut. Optimum soil temperature for good germination of groundnut is 30°C. The low temperature at sowing delays germination and increases seed and seedling diseases. A soil test must be done before starting a groundnut farming.
Crop rotation is very important in groundnut farming, this helps in efficient nutrient utilization and reduces soil-borne diseases and nematodes. It also helps to reduce the incidence of weeds. Maize, sorghum, pearl millet or small grain crops can be grown following groundnut. To reduce the incidence of soil-borne diseases it is recommended not to grow groundnut after groundnut, or tobacco, or cotton.
In Groundnut farming, a balanced fertilizer application, based on soil tests, should provide adequate levels of especially phosphorus, potassium, calcium, sulfur, and magnesium. Nutrient availability depends on soil pH, organic matter content, and rate of release of nutrients from the soil minerals. The availability of other essential ions such as copper, boron, iron, manganese, and nitrogen may be low in alkaline soils (pH >8.5); while an acid soil (pH <6) may be deficient in molybdenum, manganese, sulfur, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and calcium. Therefore, depending on soil nutrient status and the targeted yields.
You may also like Solar Subsidy, Loan Schemes for Agriculture.
In Groundnut farming, application of 1 0 – 1 2 t ha-1 of chicken manure or 20 t ha-1 of well-decomposed farm yard-manure should be used and completed at least 1 month before sowing. This should be mixed into the soil for good plant development and to improve the soil structure.
The main Fertilizer components in Groundnut Farming are Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Sulphur, Iron, Zinc. Deficiencies of boron, copper, molybdenum, manganese, and magnesium can be corrected by soil application of these nutrients when symptoms appear, depending on soil type and agroclimatic conditions.
When testing for yield and quantitative characters, treatments are to be randomized and arranged in the plots in blocks. The plot size is four rows of 4m length, with 30 cm between rows and 10 cm between plants.
The experimental field maps indicating the randomization of treatments, blocks, the direction of rows, number of rows, row width, row length, and alley width are prepared. Next, the seed and fertilizer packets for each row are prepared.
Bold and well-filled pods are selected for shelling about one week before sowing. The viability of the kernels may deteriorate after being shelled and stored for a long time and are more subject to storage pest damage. The plants produced from bold kernels were found to be superior to those from correspondingly smaller kernels in their rate of emergence, number of successful seedlings, number of primary branches and leaves, and dry mass of roots, shoots, total dry matter, and pod yield.
To control pathogens causing seed and seedling diseases, it is necessary to coat the seed before sowing with either Thiram® (a.i. 5 0 % @ 3 g kg -1 seed) or Bavistin® (a.i. 5 0 % @ 2 g kg’ 1 seed). Seed may be inoculated at the time of sowing by field inoculation to ensure good nodulation where the soil has been found to contain few rhizobia.
The seed rate depends on the variety (Spanish, Valencia, or Virginia), runner or bunch type, the seed mass, and germination rate of the seed-lot. The recommended population for bunch varieties is 330 000 plants ha -1 (about one plant per 30 x 10 cm). In case of semi-spreading and spreading varieties the recommended population is 250 000 plants ha -1 (one plant per 40 x 10 cm).
Sowing by hand is done the calculated amount of seed for each row is separately packeted and the packets for each plot are temporarily fastened together. In the case of machine sowing, seed packets are arranged by groups of rows for continuous sowing.
You may also check the Smart Farming Techniques in India.

You may also like the Betel Leaf Farming, Planting, Care, Harvesting.
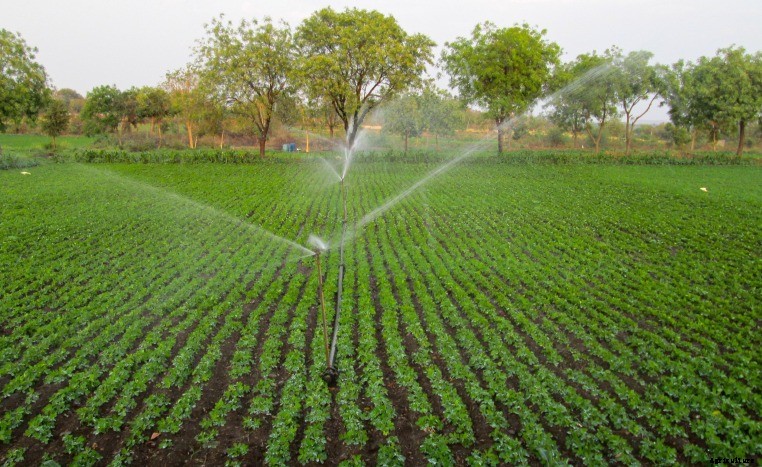
The aim of irrigation is to prevent soil water deficit and to supply the crop’s upper rooting zone with sufficient moisture without waterlogging the root zone.
It is not too late to check the Organic Tobacco Cultivation.
Weeds cause much damage to the groundnut crop during the first 45 days of its growth. The most critical period of weed competition is from 3-6 weeks after sowing. The average yield loss due to weeds is about 30%, whereas under poor management yield loss by weeds may be 60 %. Therefore, it is advantageous to mechanically and chemically control weeds during the initial 6 weeks of groundnut growth.
Premature harvesting of groundnut pods lowers the yield, oil percentage, and quality of seeds. Delay in harvesting after physiological maturity can result in increased Aspergillus flavus infection, and aflatoxin contamination in pods/seeds, and many pods may be left in the soil due to a weakening of pegs. The Spanish bunch varieties (nondormant types) start germinating if harvesting is delayed. Therefore, it is important to harvest at optimum maturity.
There are three ways of harvesting in Groundnuts
Note: Harvested plants should be stacked in the field for a few days for air and sun drying (on bright sunny days) before stripping the pods. Thereafter, pods are continuously dried to reach a moisture content of 6 – 6 % to avoid the development of aflatoxin caused by yellow mold (Aspergillus flavus). On cloudy days, pods should be removed and immediately placed in the air drier at 27-38°C for 2 days or until the pods dry to a constant mass (6 – 8 % moisture).
After cleaning and grading, store the dry pods in gunny bags and stack them up to 10 bags high in separated stacks so that air freely circulates among them. The bags should be piled on wooden planks to avoid damage from dampness. Dusting the bags with 5% Lindane® will protect the pods from many storage pests.
Marketing is easy where you can sell to local Groundnut mills or Agents or Government markets.
You may be interested in How to Grow Tomatoes without Soil.