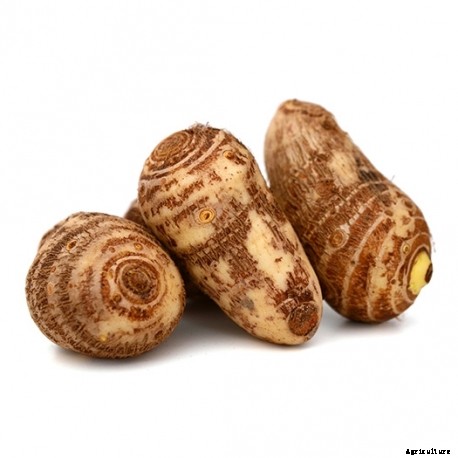

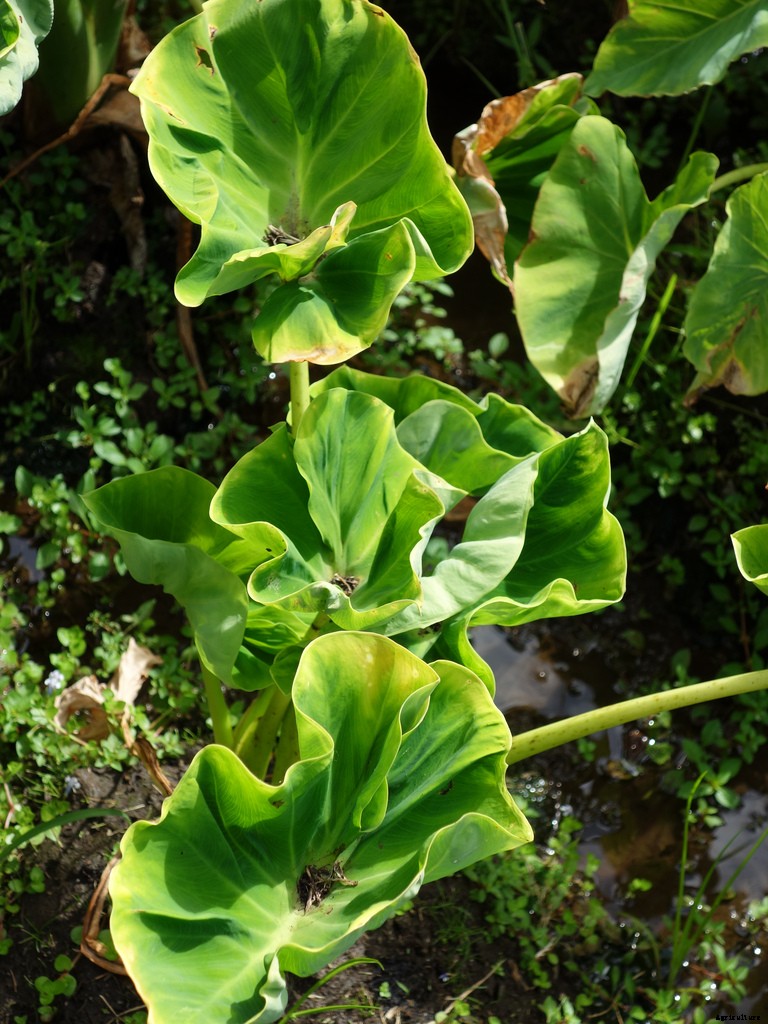
It is a perennial herbaceous plant which is grown in tropical and subtropical regions. It requires warm season for its growth. It is commercially grown because of its consumption of sweet and starchy tubers. Arvi is also known as Taro and the Taro roots are also known as “eddo”, “dasheen” and “kalo”. The plant mainly attains the height of 1-2m. They have light green color leaves which are elongated and heart shaped.
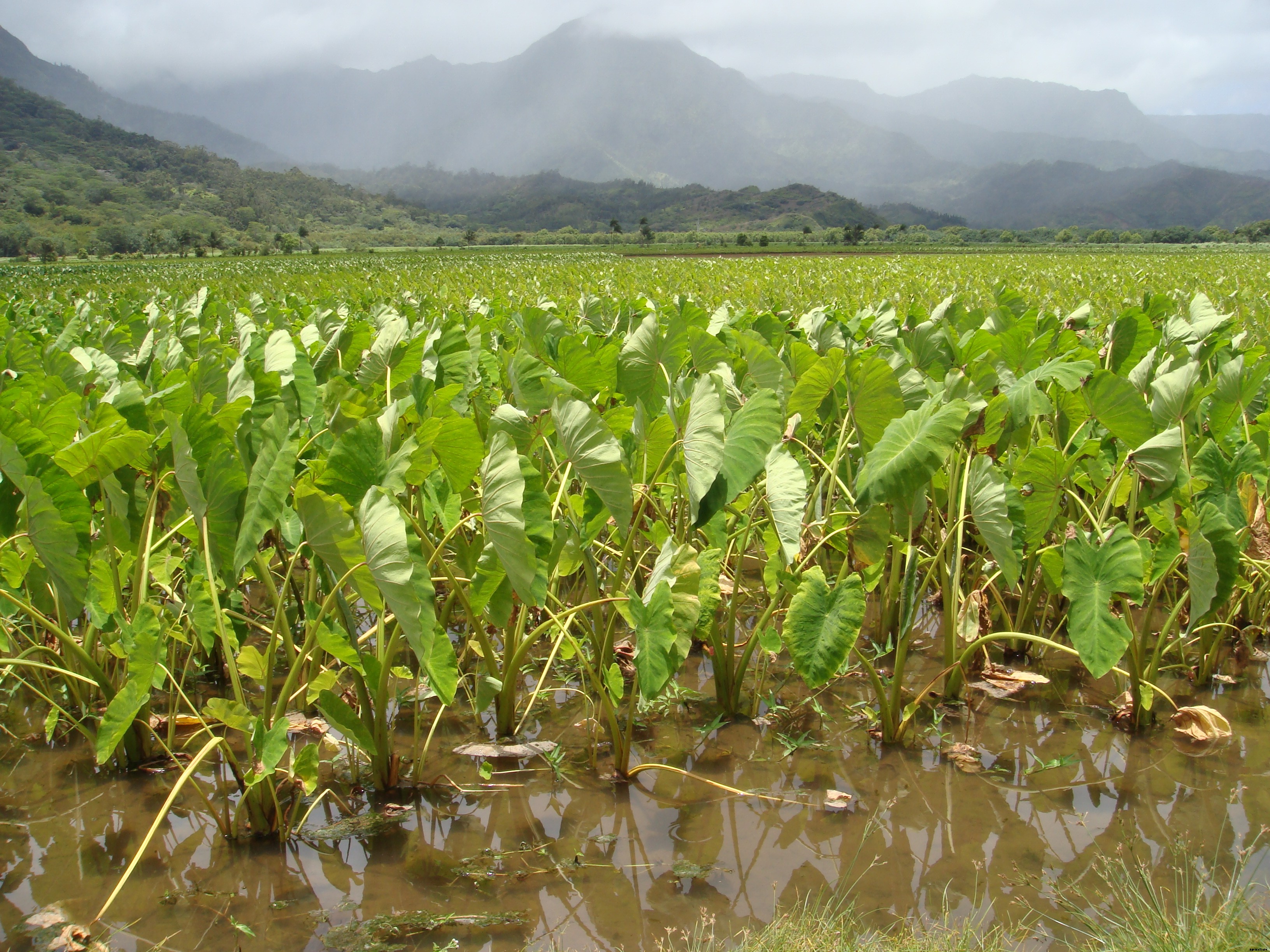

Temperature 18-35 °C Rainfall 120-150 mm Sowing Temperature 18-22 °C Harvesting Temperature 25-35 °C
Arvi is planted in variety of soil ranging from sandy to loamy soil. But the best results it gives when grown in sandy loam or loamy soils having high organic matter. Avoid cultivation in soil having poor drainage system. Soil which lacks in fertility and moisture results in low quality corm yield.
Punjab Arvi-1, Sree Pallavi, Sree Kiran, Sree Rashmi
For Arvi plantation, the land should be well prepared. To bring the soil to the fine tilth, before sowing land must be ploughed 2-3 times followed by planking’s. The field should be kept weed-free.
For optimum yield, tubers should be sown in nursery beds in the first fortnight of February under Punjab conditions
Use row to row spacing of 60 x 15 cm or 45 x 20 cm.
Use depth of 6-7.5 cm for tuber planting.
The corms are sown manually, deep in the soil. Dibbling method is used for sowing corms. Beside this its sowing is also done with potato like machine used for sowing
Use 300-400 kg of tubers in per acre land.
For seed treatment dip the tubers in 2% solution of Bavistin for 30 minutes. It protects the tubers from the soil borne diseases.

Apply well rotten FYM (Farm Yard Manure) @5-7tonnes/acre before sowing. Along with FYM apply fertilizer dose in terms of Urea @90kg/acre, SSP @125kg/acre and MOP @35kg/acre.
Full dose of K2O and P2O5 is applied at the time of planting. Nitrogen dose is applied in 2 splits i.e. first at the time of sowing and remaining half should be applied at the time of hoeing and weeding.

To make the field weed free, 1-2 hoeing’s and earthing up should be done after each hoeing.

Pre-requisite irrigation is necessary for good yield of crop. In summers, irrigation is given at the interval of 3-4 days and in rainy season, no irrigation required but sometimes lifesaving irrigation is necessary. Arvi requires constant irrigation for regular sprouting therefore immediate irrigation is required after sowing. Keep the field wet till seedling germination.
The disease mainly occurs during rainy season when night temperature is between 20-22°C and day temperature is between 25-28°C. The symptoms are water soaked circular lesions are seen which become yellow or dark purple color when dried.
Use of Dithane M-45 @400-500 gm/acre in 100-150 ltr water should be applied at the interval of 7-14 days to get cure form leaf blight.
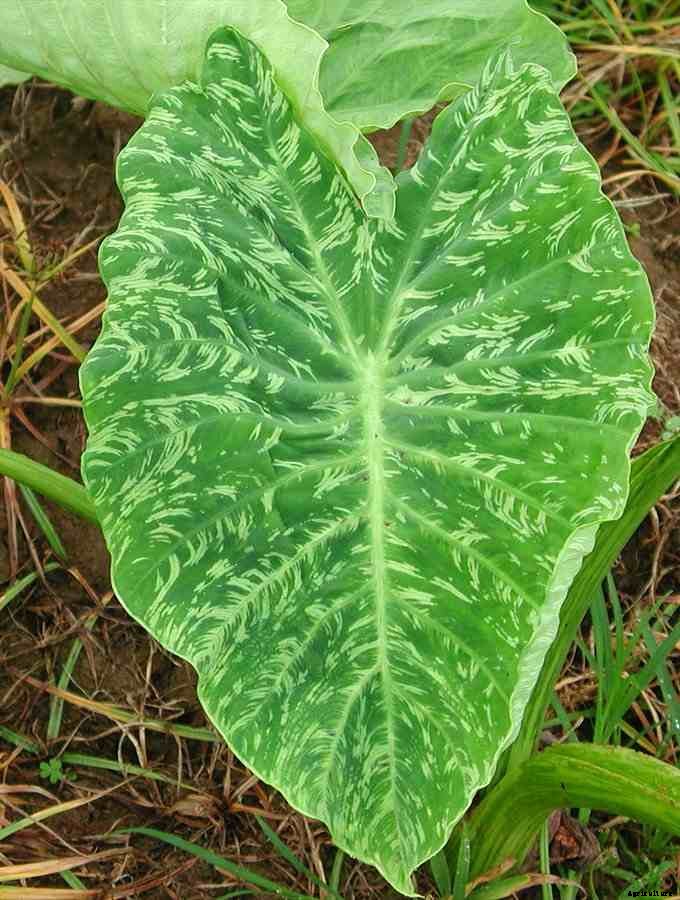

It is a viral disease which is carried out by aphids. The symptoms are seen more in cooler months and the symptoms are veinal mosaic and dispersed pattern seen on the foliar leaves. Treatment: Different varieties of arvi crops should be grown to avoid Dasheen Mosaic Virus.

It is a viral disease caused by bacilli form virus. The symptoms are crinkled and conspicuous feathery mosaic on young leaves.
Rouging is one of the methods to prevent from this virus or resistant varieties should be grown to get rid from Alomae/Bobone Virus.
The symptoms are stunted growth, shortened leaf stalks, curled and crinkled leaf blades and yellowish and spotted leaves.
Use of Captan 50WP @44-45 kg/acre is used to treat corm rot.
The pests attack the seed corms which will result in poor seed production.
Use of Malathion 50EC @250 ml/acre will help to control insect pests.
Harvesting is mainly done after 175-200 days of sowing i.e. when leaves become yellow in color. To obtain soft corms, early harvesting should be done. Proper moisture in the fields is necessary for easy harvesting of corms. Harvesting of corms is done with the help of spade or other hand tools. After harvesting, corms are cleaned and then grading should be done.
Secondary corms are stored in cool and dry place for seed production purpose. By storing in cool and dry places it will help to protect corms from rotting. It can also be stored in cold storages or in pits.