Soil, a valuable resource, is the topmost layer of Earth’s crust. A thin layer of soil is formed on the surface of earth, by various processes of weathering and gradation of the parent rock material.
A soil is a mixture of rock debris and organic matter that forms on the earth’s surface. Relief, parent material, climate, vegetation, and other life forms all contribute to soil formation. Apart from these factors, human activities also have a significant impact on formation of soil. There are four elements in soil: minerals, humus, water, and air.
Soil is divided into layers of subsections which are called as “horizon“. For example, if we are able to dig a deep enough hole / pit in the ground, we will notice variations in colour of the soil. All these different coloured layers of soil are individually called horizons and all these horizons when considered together is called soil profile of that particular location.
Soil profile (layers of soil or cross section of soil) is depicted in the following diagram:
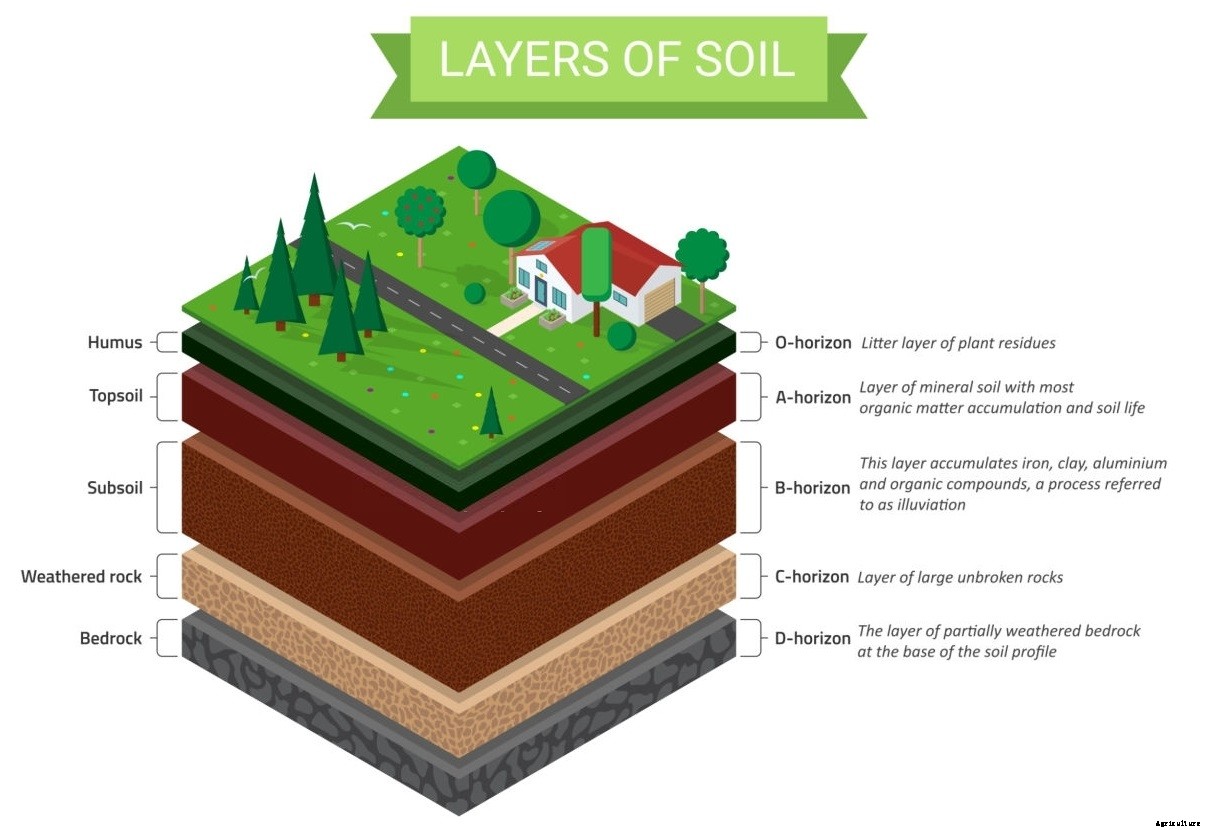


In 16th century AD, soil was classified on the basis of inherent characteristics and external features. External features included colour, texture, moisture content of the soil and slope of the land.
Texture of the soil was further classified as clayey, silty, sandy and loam. Colour of the soil was further classified as black red or yellow.
In ancient times, soils of India were classified mainly in two catagories:
The National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning – (NBSS&LUP), an institute constituted under Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), assisted ICAR in classification of Indian soil based on the standards laid out by United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Soil Taxonomy.
| ICAR has classified the soils of India into the following order as per the USDA soil taxonomy | ||
|---|---|---|
| ORDER | AREA (in Thousand Hectares) | PERCENTAGE |
| Inceptisols | 130372.90 | 39.74 |
| Entisols | 92131.71 | 28.08 |
| Alfisols | 44448.68 | 13.55 |
| Vertisols | 27960.00 | 8.52 |
| Aridisols | 14069.00 | 4.28 |
| Ultisols | 8250.00 | 2.51 |
| Mollisols | 1320.00 | 0.40 |
| Others | 9503.10 | 2.92 |
| Total | 100 | |
| Source : Soils of India, National Bureau of soil survey and land Use Planning, publication Number 94 | ||
In 1956, All India Soil Survey Committee was formed by The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR). This committee categorized types of Indian soil in 8 major categories. These logical and widely accepted categorizations were made on the basis of the soil genesis, composition and location, and colour.

| KHADAR | BHANGAR | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | New alluvial deposits in Northern plains | Old alluvial deposits in Northern plains |
| Stability of deposit | Not stable | Stable |
| Location | Near the river bed | Away from river bed |
| Fertility | More fertile | less fertile |
| Renewal of deposit | Renews every year | Does not renew |
| Suitability for agriculture | More suitable | Less suitable |
| Concentration of Kankar on Calcium carbonate | Less | High |
| Texture | Coarse | Fine |








Following table represents state-wise distribution of soils of India. It also depicts certain characteristics (such as content availability in the soil and preferred crop to grow on the soil).
| SOIL TYPE | SURPLUS MINERALS / ELEMENTS | DEFICIENT MINERALS / ELEMENTS | RECOMMENDED CROP | INDIAN STATE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alluvial Soils | Potash, Lime | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Organic matter | Rice, Wheat, Sugarcane, Tobacco, Cotton, Jute, Maize, Oilseeds, Vegetables, Fruits | Plains of Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana, UP, Bihar, Jharkhand |
| Black soils | Lime, Iron, Magnesia, Alumina, Potash | Nitrogen, Potassium, Phosphorous, Humus | Cotton, Wheat, Jowar, Linseed, Virginia tobacco, Castor, Sunflower, Millets | Deccan plateau- Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh,Tamil Nadu, Valleys of Krishna and Godavari. |
| Red and Yellow Soils | Iron, Potash | Nitrogen, Humus, Phosphoric acid, Magnesium, Lime | Cotton, Wheat, Rice, Pulses, Millets, Tobacco, Oilseeds, Potatoes, Fruits | Parts of Tamil Nadu, Southern Karnataka , South-East Maharashtra, parts of Madhya Pradesh, Goa, Kerala, Orissa, Bihar, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Eastern Parts of Rajasthan, Assam, Manipur, Tripura, Meghalaya and Nagaland |
| Laterite Soils | Iron oxide, potash, Aluminum, Titanium, Manganese oxides | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Lime, Magnesia, Organic matter, Calcium | Tea, Coffee, Cashew, Rubber | Karnataka, Kerala, Tamilnadu, Madhya Pradesh, Assam and Orissa hills. |
| Arid Soils or Desert soils | Sodium, Phosphate, Gypsum, calcium carbonates | Humus, Nitrogen | Barley, Cotton, Wheat, Millets, Maize, Pulses | Western Rajastan, north Gujarat and southern Punjab |
| Saline Soils or Alkaline Soils | Sodium, Potassium, Magnesium | Nitrogen, Calcium, Phosphorus | Date palm, Barley, Sugarbeet, Cotton, Asparagus, Spinach | Western Gujarat, deltas of eastern coast, Sunderban areas of West Bengal, Punjab and Haryana |
| Peaty Soils | Aluminum Sulphates, Carbon, Nitrogen | Copper, Boron, Zinc | Potatoes, Sugarbeet, Celery, Onions, Carrots, Lettuce, market garden crops, Willows | Orissa, Sunder-bans in West Bengal, parts of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Kottayam, Alleppey, districts of Kerala |
| Mountain Soils or Forest Soils | Phosphorus, Calcuim, Magnesium, Pottassium, Sulfur, Manganese | Phosphorus, Potash, Lime | Rice, Tea, Beans corn, Squash, Vegetables | Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, W estern Ghats in Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu |